
Intel Corp. officially announced Kaby Lake, its seventh-generation Core PC processors made in a 14nm+ process and focused on delivering better 4K video. The family provides the first indication of what more modest product advances may look like as Intel stretches Moore’s law to cover with one process node multiple generations of chips.
Kaby Lake processors gain a 12% improvement from enhancements to Intel’s 14nm process. They also include a modestly updated media engine with hardware support for decoding VP9 video and encoding and decoding 4K 10-bit HEVC video. Otherwise, the chips use the same architecture as the previous Skylake generation, including the existing Skylake x86 pipeline.
The new generation is the first to break Intel’s tick-tock cadence of alternating between a new process node and a new microarchitecture every year. With the increasing complexity and costs of pursuing Moore’s Law and a slowing PC market, Intel decided to stretch one process generation across three years and three families of chips.
The 14+nm process delivers transistor-level enhancements such as taller fins and improved gate pitch, interconnect speed and aspect ratio to deliver 12% better performance. At its Intel Developer Forum earlier this month, the company said it plans to make product families in three generations of its emerging 10nm process.
At the systems level, Kaby Lake should enable 19% faster browsing and photo editing. Systems should deliver 4K resolutions for games running at 35 frames/second and support 4K movie playback for up to 9.5 hours.
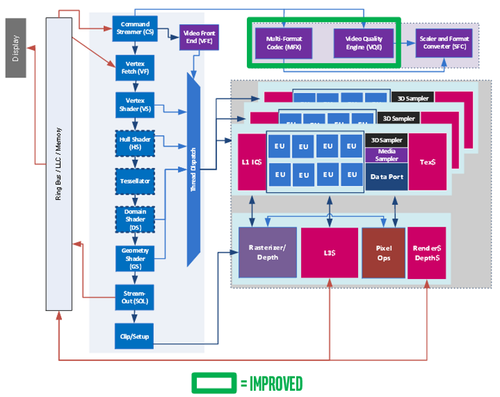
Intel updated two blocks on the Skylake media engine focused on video acceleration. (Image: Intel)
Mobile Kaby Lake processors running at 4.5W-15W are shipping now with systems using them expected this fall. Higher-end notebooks and desktops with up to 65W processors will follow early next year.
Many of the systems will sport innovations not directly related to the new processors. For example, as many as 120 designs are expected to use the Thunderbolt 3, a 40 Gbit/second link using the USB Type C connector. More than 50 systems are expected to adopt 4K panels and fanless notebooks such as the Asus Transformer 3 are expected to measure less than 7mm in thickness.
Intel said the new systems will deliver “more than 70 percent faster mobile productivity than a 5-year-old PC and 3.5x better 3D graphics performance than a 5 year old PC.”
The comparisons deflect attention from the lower performance numbers compared to last year’s 14nm Skylake chips. They also hope to encourage upgrades from users holding on to their systems longer than in the past.
----Form EE Times